What is inflammation?
Inflammation is the body’s response to threat or injury, and it’s not always a bad thing. If you fall while playing basketball and twist your ankle, your body will produce swelling (inflammation) around the ankle to direct resources for healing and protection.
In times of crisis or acute injury, inflammation serves a wonderful purpose! It warns us and urges us to remove or avoid the threat. However, chronic and excessive inflammation harms the body, including the brain!
Here is how it works. When trauma occurs, the body sends out pro-inflammatory proteins called cytokines to neutralize the threat. When physical trauma starts healing and all bacteria have been killed, the amount of cytokines goes down, inflammation stops, and the system returns to normal balance.
But with depressed patients, the brain and the entire nervous system stay in continuous fight or flight mode, perpetuating the production of cytokines that, coupled with stress hormones, damage neurons and change the way our brains function. We become lethargic, have trouble concentrating, and feel stuck.
Luckily, we are not stuck. There is a plethora of ways to decrease inflammation and restore our bodies’ natural balance. Here are some of these ways:
1. Juicing
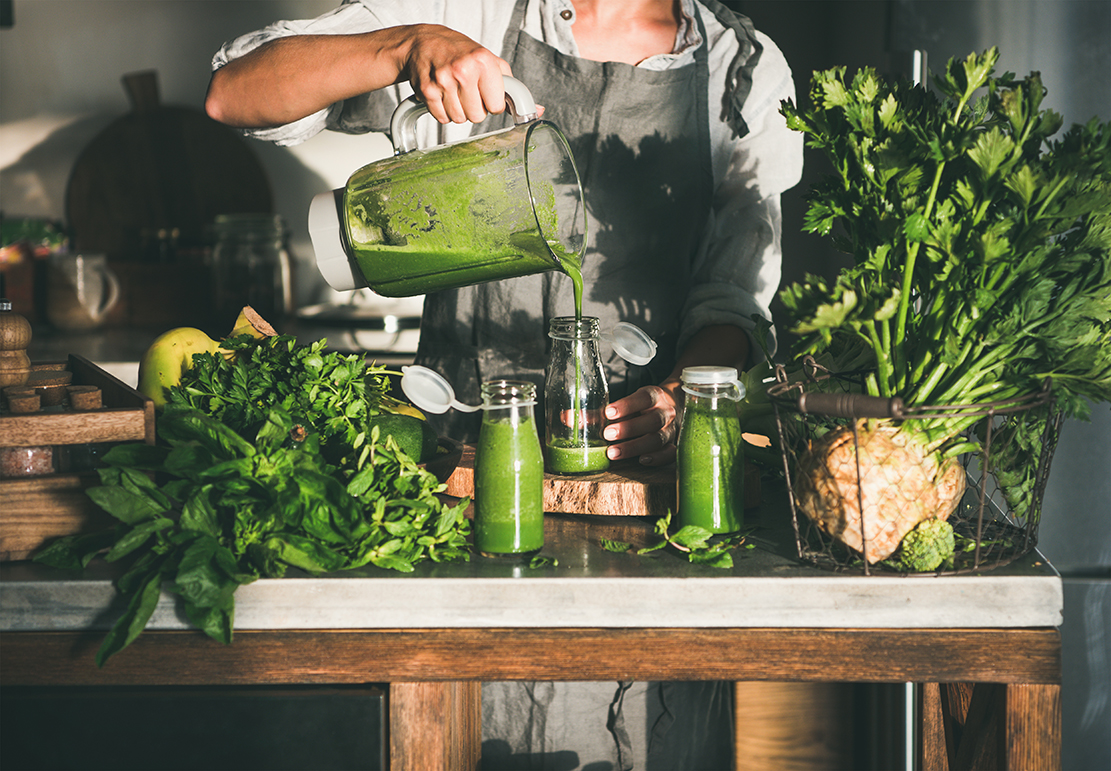

Juicing your own carrots and other vegetables gives your body the antioxidants and vitamins needed to fight infections and manage inflammation acutely rather than suffering from chronic inflammation.
2. Essential Fatty Acids
Increasing essential fatty acids, found in foods like salmon and similar cold water fish, reduces and controls your body’s inflammatory response to infection and may decrease depression.
3. Probiotic Supplementation
Probiotic supplements, especially multiple strain varieties, are great for boosting energy and the immune system to curb inflammation.
4. Probiotic Foods
Probiotic foods regulate the gut, reducing sugar and carb cravings and improving metabolism while competing with and decreasing the inflammatory toxins released by harmful bacteria. Indirectly, probiotic-rich foods are natural stress relievers – the gut makes most of the serotonin in the body (the “feel-good” neurotransmitter). That only happens if we have healthy bacteria working with our digestion.
5. Phyto-Nutrients
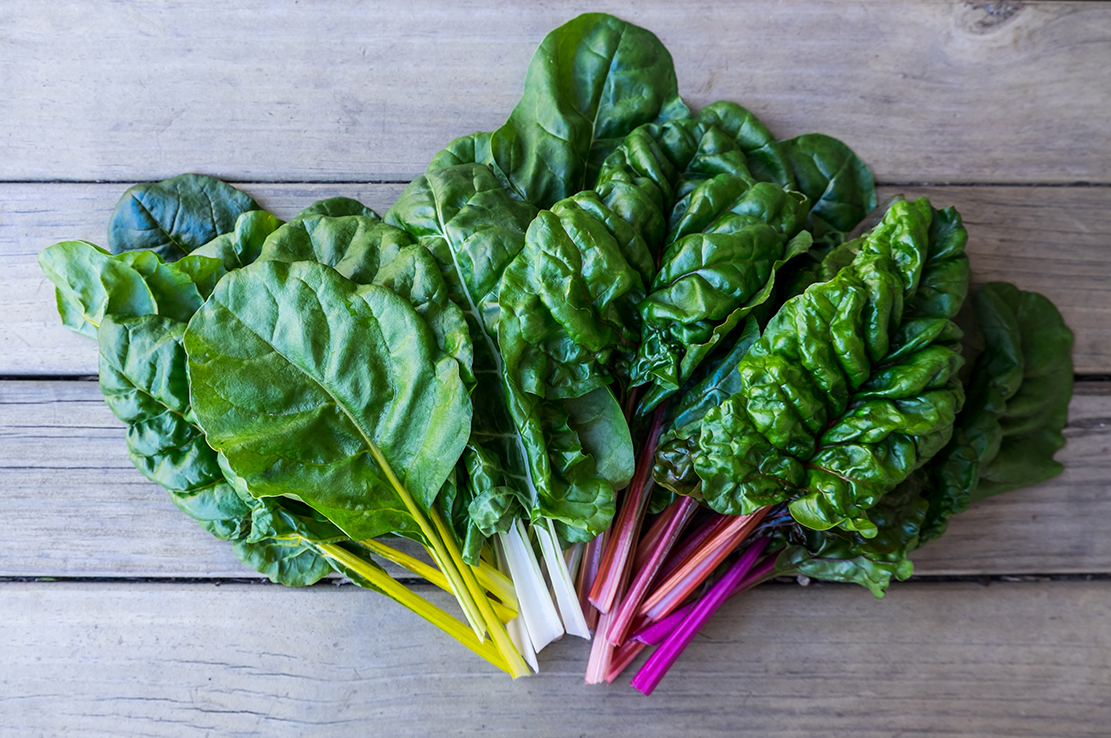

Eat foods high in phytonutrients for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Phyto-nutrients are chemicals that plants use to fight disease. The best known phytos are found in colorful fruits and vegetables as well as dark green leafy vegetables and sea vegetables.
6. Green Tea
Aim for 2-5 cups of tea per day for its anti-inflammatory effects. Choose Matcha green tea, which is completely unfermented.
7. Reishi
Researchers found that Reishi (a mushroom) could be effectively used to improve the immune system and treat stiff necks, stiff shoulders, conjunctivitis, bronchitis, and rheumatism, without any significant side-effects. In order to reap the anti-inflammatory properties of Reishi it is best to take the liquid extract form, which can be added to coffee or tea.
8. Boswellia
Boswellia is an herbal extract that blocks pro-inflammatory agents. It is generally taken orally as a capsule or decoction – a method of extracting the nutrients by boiling the plant’s bark.
9. Turmeric
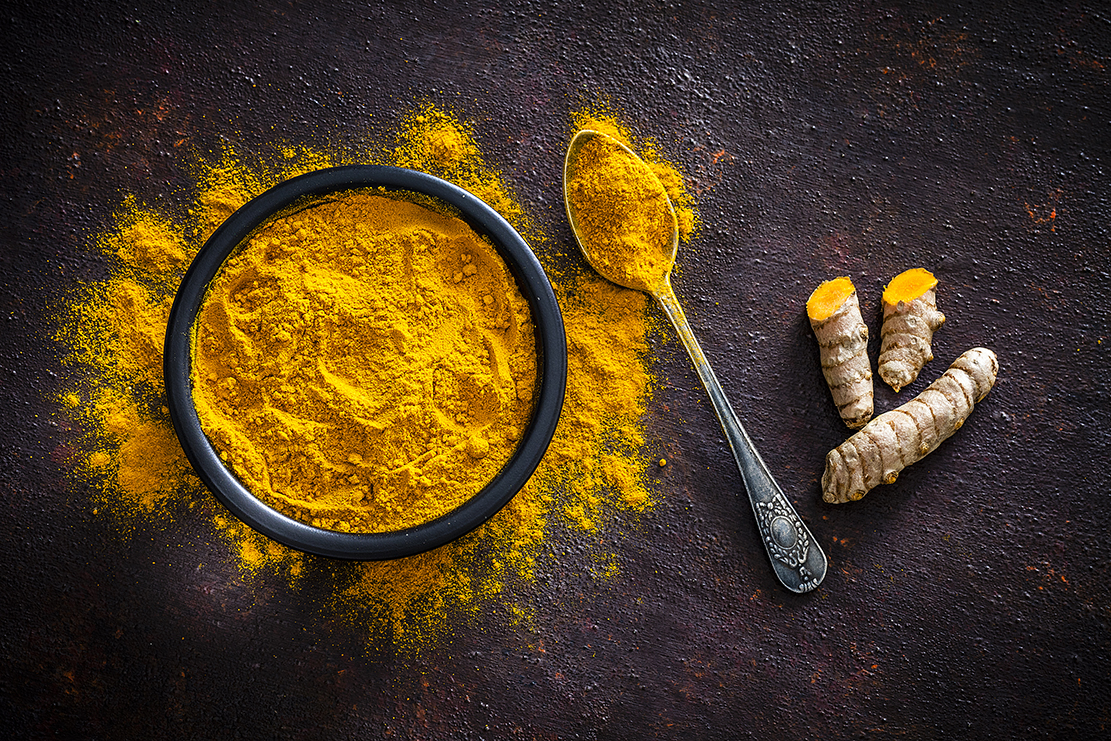

The orange pigment in turmeric is called curcumin, which has been shown in studies to be as effective at reducing inflammation as common anti-inflammatory drugs. Turmeric makes for a great spice when cooking and can be used in teas or lattes. Curcumin can also be taken as a supplement.
10. Fish Oil
Fish oil shuts down inflammatory pathways. Use a high-quality fish oil such as Life Extension, Green Pastures, or Garden of Life. Aim for 2-4 grams EPA/DHA per day.
11. Other Anti-Inflammatory Foods
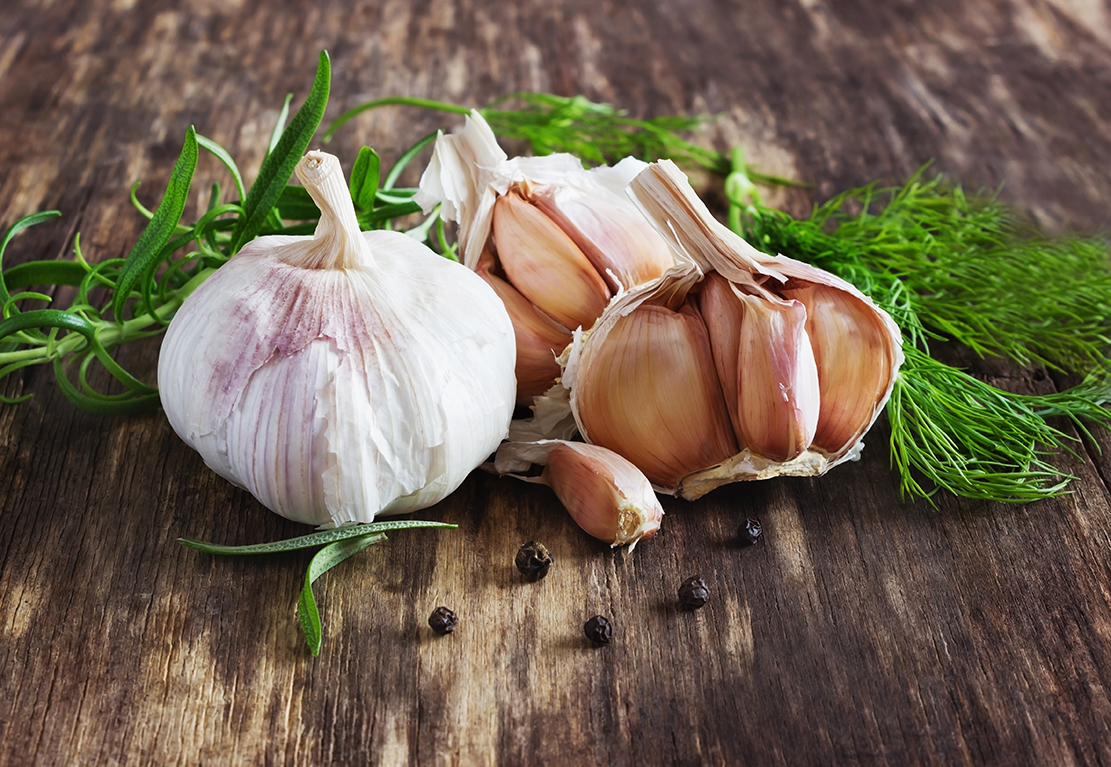

Some other high anti-inflammatory foods are capsicum (from cayenne pepper), ginger, garlic, dill, walnuts, and chia seeds.
Aside from changes in nutrition, there are other proven ways to reduce inflammation and return to balance.
Other inflammation fighters:
- Massage therapy
- Earthing
- Essential oils
- Acupuncture
- Breathing exercises
- Yoga
- Meditation & Mindfulness
- Emotional release work







Very helpful article I have severe nueropthy and issues with my digestive system. It is definitely difficult for me. Thank you for the advice.
Thank you! We hope these tips will help you greatly.